Cybersecurity
SMART CITY SOLUTIONS
AND TOOLS
Introduction
Cybersecurity in the context of a smart city refers to any data leakages originated from attacks or bad actions leading to malfunctioning of digital systems and violence of data protection of citizen’s relation to governmental bodies.
Description
Smart cities promote the city’s collective intelligence by connecting physical infrastructure with IT services towards establishing an ecosystem of urban services. Smart City improves citizens lives by automating municipal duties, improving communication between governmental bodies and citizens, decreasing consumption of resources or removing financial burdens.
The backbone of a smart city is the various IoT (Internet of Things) network sensors deployed in the infrastructure and provide raw data for different sectors (health, transportation, governance, grid).
Cybersecurity is about protecting the devices people use, the information stored and processed in these devices, and the identity of people using these devices. Cybersecurity threats can be divided into three main categories: Cyber-Crime targeting systems for monetizing or sabotage, Cyber-attack for gathering information (politically motivated) and Cyber-terrorism aiming to create intimidation. Typical methods against cybersecurity include Malware (viruses, spyware, adware and botnets), DoS attack, SQL injection, social engineering, etc.
- Security alert systems, street video surveillance and smart traffic lights are considered as the most vulnerable to cyberattacks with high impact.
- Real Case: In January 2021, in Florida, the local water supply system was shut down due to chemical concentrations coming from malicious attack.
- Real Case: Atlanta city systems were hacked, and data encrypted by ransomware, authorities were asked to pay a ransom to get data back.
Applications of cybersecurity
- Transportation
- Critical Infrastructure
- Physical security
- Telecommunications
- Government
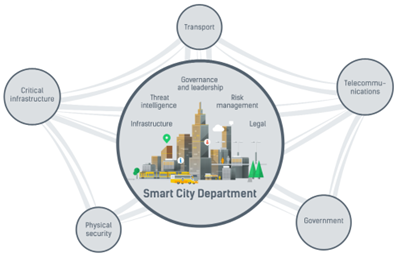
Image source: Securingsmartcities.org
Advantages and challenges
+ Secure Smart Government applications reduce crimes by increasing the level situational awareness, efficient response to accidents, improving municipal services.
+ Secure Smart Healthcare solutions can connect people and health facilities. It can improve patient remote monitoring, diagnosis and treatment, hospital management services.
+ Design urban digital systems to establish privacy by restricting the collection of anonymised personal data and deploying stricter data encryption techniques.
– Smart buildings, as a subsystem of the smart grid, are vulnerable to privacy breaches.
– Lack of policies or standards allows cities to experiment with new products that create interoperability and integration problems – vulnerable for cyberattacks.
– Each city is unique and must take its own approach to address cybersecurity issues. However, there are some principles and best practices defined on city level (Model Policy for Cyber Resilience in Local Government).
References
- Smart City Security: Atlanta Cyberattack Cripples City
- Uchendu, B., et al., 2021. Developing a cyber security culture: Current practices and future needs
- Gunes, B. et al., 2021. Cyber security risk assessment for seaports: A case study of a container port
- Huang, J., et al., 2020. Secure remote state estimation against linear man-in-the-middle attacks using watermarking


