Wind Energy
RENEWABLE & ALTERNATIVE
ENERGY SOURCES
Introduction
Turbines are windmill-like structures that use wind to drive a three-bladed rotor. The rotor is attached to a generator that converts the energy to electricity. Wind energy is currently one of the cleanest and sustainable forms of electricity generation available. Wind power is harvested in windy regions, by the shore or in sea.
Description
Wind energy is generated by converting wind currents into other forms of energy like electricity, using wind turbines. Turbines extract kinetic energy from the blowing air and converts the rotational movement via a rotor into electricity, which is then passed onto the utility grid for consumption. Today wind turbine blades are made from fiber-reinforced epoxy, or unsaturated polyester. In recent times, turbines have also been developed to float out at sea, rather than just land based, thus reducing the visual impact of such installations.
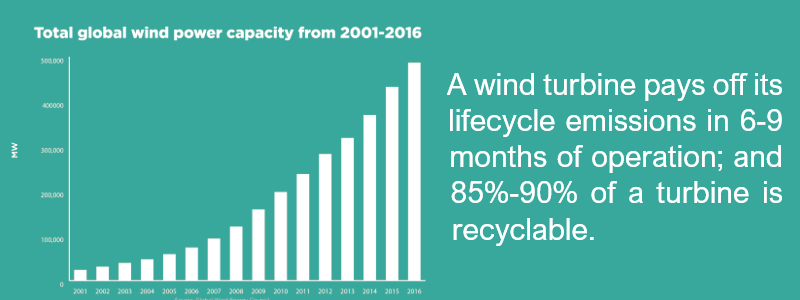
Wind energy projects produce 95% less CO2 than electricity from gas, and 98% less CO2 than electricity from coal. The modern wind turbine converts 45-50% of its input into electricity. Coal-fired power stations generally convert around 29-37% of their input. The CO2 footprint is negligible and turbines hardly consume any water.
Main Features
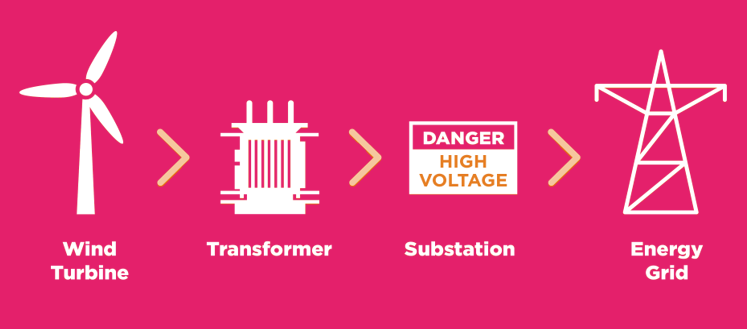
- Wind turbine
- Transformer
- Substation
- Energy grid
Advantages and challenges
+ Wind energy is a clean fuel source.
+ Wind power is cost-effective and sustainable.
+ Wind creates jobs and a domestic source of energy.
– Wind power must still compete with conventional generation sources on a cost basis.
– Good land-based wind sites are often located in remote locations.
– Wind energy is an intermittent source.
– Wind resource development might not be the most profitable use of the land.
– Turbines can cause noise and aesthetic pollution.
– Wind plants can impact local wildlife.


