Heatwaves
BEHAVIOURAL ADAPTATION TO
EXTREME WEATHER

Introduction
Extended periods of high temperatures are becoming more frequent and intense all over the world. This process is fast forwarded with the climate change. Heat stress affects the vulnerable population the most. Heatwave intensity is a major public health issue in high urban areas. More expanded green areas can help mitigate the negative health impacts of heatwaves.
Description
A heatwave refers to a period of extreme and unusual warmth which can lead to heat stress and serious implications for human health. Heat-related mortality occurs when the body’s ability to cool itself through increased perspiration and blood circulation cannot keep up with a rapid rise in ambient temperature. Heat stress affects the vulnerable like the elderly, the young, and persons with mental diseases or chronic illnesses the most.
Heatwaves are not only affected by the climate but also urban land uses. Urban areas are places where a large number of people and property are concentrated, and can be quite sensitive to heat waves due to the urban “heat island effect”. At 1.5°C of warming, 2.3 billion people could be vulnerable to heatwaves, with negative impacts on their health and productivity. Green city elements like trees, green roofs, and vegetation can help reduce urban heat island effects by shading building surfaces, deflecting radiation from the sun, and releasing moisture into the atmosphere.
“Redesigning urban landscapes with more vegetation and water and implementing passive cooling strategies to improve thermal performance and reduce energy consumption in buildings are key to making cities more resilient to heatwaves.”
Jonathan Duwyn, head of the Cities Unit at UNEP.
Main Features
Types of heatwaves based on intensity:
- Low-intensity heatwaves – most people can cope.
- Severe heatwaves – challenging for vulnerable people.
- Extreme heatwaves – dangerous for people who do not take precautions to keep cool and work outdoors.
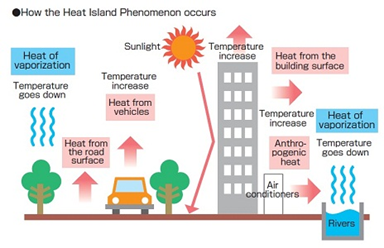
Image source: gardinergreenribbon.com
Advantages and challenges
Green City Elements can help reduce heatwaves which can be mitigated by:
+ Undertaking urban planning and green infrastructure improvements into regular street upgrades and capital improvement projects.
+ Undertaking tree canopy assessments to use trees to address urban heat, stormwater management, and other concerns.
+ Painting buildings with light colours that absorb less heat.
+ Planning urban forestry and vegetation initiatives in busy urban areas.
+ Building of green roofs to decrease the thermal load.
– The rate of climatic change is generally occurring too quickly for many species to adapt.
– Hard to change city design, urban and emergency planning from the grassroots.
– Poor understanding of community-related factors.
– Cash flow and resource issues that stall ambitious projects.
– Older adults may face more challenges than most in reaching consultation efforts.
– Competing issues for public space, and indifference from public and private entities.

