Solar Energy – Photovoltaics
RENEWABLE & ALTERNATIVE
ENERGY SOURCES

Introduction
Solar panels can generate electricity from solar energy. The delivered power depends on the size and type of panels, the intensity of solar radiation, wavelength and angle of incidence. Photovoltaics (PV) can substitute traditional energy sources.
Description
Based on the amount of feed-in power in the photovoltaic system, there can be domestic small-scale solar power plants and larger solar power plants. The two main components that are required for PV systems are solar modules and inverters.
In households, solar modules are connected in series or parallel on the house roofs in general. In the urban environment, you can find them on roofs over parking areas or on the ground in enclosed areas. From a technological aspect, there are different types of solar panels: thin-film technologies, multicrystalline or monocrystalline silicon panels; with average lifespans of 25-30 years.
Inverters are necessary for transforming direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) and regulating voltage and frequency. There are two main types of inverters, single- and three-phase inverters, which are used based on the amount of power delivered by the PV system.
In May 2022, the European Commission adopted the EU solar energy strategy alongside the REPowerEU plan to boost the use of solar energy in buildings. This plan intends to gradually introduce an obligation to install solar energy in different types of buildings over the next years.
Solar panels have lower maintenance cost compared to fossil fuels, and their investment costs can be covered in the medium term. If the cost of fossil fuels is increasing, the recovery period of PV panels is reducing. Before installing solar panels, do not forget to collect information about the regulations of your service provider and national tax
legislation.
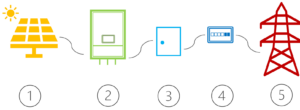
Main Features
- Solar Panel
- Inverter
- Switch Box
- Meter
- Electrical Grid
Advantages and challenges
+ PV systems can reduce the energy bills of both households and public buildings.
+ Although the generated electricity decreases slightly over time, solar panels still have 80-90% of their original output after 25 years.
+ PV systems installed in the city can reduce greenhouse gas emission in urban areas significantly.
+ A standard 25-year warranty usually covers weather damages to PV panels.
– Power generation is affected by weather conditions, and, without energy storage, PV systems cannot be the sole energy source of a building.
– The whole life cycle of PV panels cannot be considered clean, and there are still uncertainties related to environmental impacts.
– Before installation, the major challenges are related to the extraction, manufacturing and transportation of the raw materials, and the amount of used energy.
– In case of PV systems installed on the ground, the used area can suffer from degradation of the soil and reduction of biodiversity.
– Disposal of the used solar panels is another challenge. Waste management and recycle are essential as PV panels contain toxic materials.
Further Information

