Circular Design
WASTE MANAGEMENT
Introduction
Circular Economy is the model in which we do not use and dispatch resources, but instead we use our resources more reasonably and in a more efficient way, reducing our waste production.
Circular design is aimed at the beginning of the resource use chain, and thus, a very important part of the whole circular economy concept.
Description
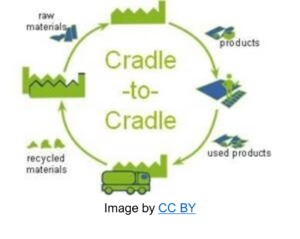
Circular design is proven to be the main challenge to implement circular economy in our cities.
Different strategies can be used towards the general public such as promotion of services via rents (or sharing, leasing, subscription, etc.), instead of buying products that are going to be used only sometimes.
Making products easier to be repaired reduce as well the number of products citizens “need” to buy. Another way is not applying planned obsolescence and extend the products’ life. Another general circular design strategy is preparing products that do not mix different types of materials, which would make products more difficult to be recycled. The use of local products that reduce the transport needs, or the production of platforms that enable citizenship to use second-hand products are other examples of strategies in the design phase of circular economy schemes. Dematerialisation to find solutions to deliver utility using the minimum amount of material possible (for example digitalization), or modularity of products, make it easier to reduce the number of resources needed.
Design is key to the first principle of circular economy, as around 80% of a product’s total environmental impact is determined in the design phase.
Main Features
- No mix of materials
- Easy to repair
- Avoid planned obsolescence
- Servilization (offer services instead of products)
- Local products
- Reuse of materials/products
Advantages and challenges
+ Asking companies and public institutions to implement circular design helps achieve circular economy objectives in the city.
+ Applying circular design in products for those citizens who are part of local companies, helps their economy (reducing resources needed), simplifies their business, and can get them revenues for selling previously considered waste products.
+ Citizens can better implement circular economy principles in their daily life with circular design products (for example, products in which no mix of material is foreseen, so it is easy to recycle).
+ Avoiding waste is often a mindset of not wanting to throw anything out, but actually, it’s an opportunity to re-think and be more efficient.
– Lack of professionals who have the relevant knowledge and experience to include these rules both in private and public sectors. General public is not really aware of circular design and how to ask for it either.
– We need to be more conscious about the materials that we use, how they’re impacting the planet and how they’re impacting us. They may not directly be affecting us right now but they will affect the generations to come.


